mirror of
https://github.com/HKUDS/VideoRAG.git
synced 2025-05-11 03:54:36 +03:00
171 lines
5.1 KiB
Plaintext
171 lines
5.1 KiB
Plaintext
Metadata-Version: 2.2
|
||
Name: imagebind
|
||
Version: 0.1.0
|
||
Summary: A brief description of the package
|
||
Home-page: https://github.com/facebookresearch/ImageBind
|
||
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: 3
|
||
Classifier: License :: Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International
|
||
Description-Content-Type: text/markdown
|
||
License-File: LICENSE
|
||
Dynamic: classifier
|
||
Dynamic: description
|
||
Dynamic: description-content-type
|
||
Dynamic: home-page
|
||
Dynamic: summary
|
||
|
||
# ImageBind: One Embedding Space To Bind Them All
|
||
|
||
**[FAIR, Meta AI](https://ai.facebook.com/research/)**
|
||
|
||
Rohit Girdhar*,
|
||
Alaaeldin El-Nouby*,
|
||
Zhuang Liu,
|
||
Mannat Singh,
|
||
Kalyan Vasudev Alwala,
|
||
Armand Joulin,
|
||
Ishan Misra*
|
||
|
||
To appear at CVPR 2023 (*Highlighted paper*)
|
||
|
||
[[`Paper`](https://facebookresearch.github.io/ImageBind/paper)] [[`Blog`](https://ai.facebook.com/blog/imagebind-six-modalities-binding-ai/)] [[`Demo`](https://imagebind.metademolab.com/)] [[`Supplementary Video`](https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/imagebind/imagebind_video.mp4)] [[`BibTex`](#citing-imagebind)]
|
||
|
||
PyTorch implementation and pretrained models for ImageBind. For details, see the paper: **[ImageBind: One Embedding Space To Bind Them All](https://facebookresearch.github.io/ImageBind/paper)**.
|
||
|
||
ImageBind learns a joint embedding across six different modalities - images, text, audio, depth, thermal, and IMU data. It enables novel emergent applications ‘out-of-the-box’ including cross-modal retrieval, composing modalities with arithmetic, cross-modal detection and generation.
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
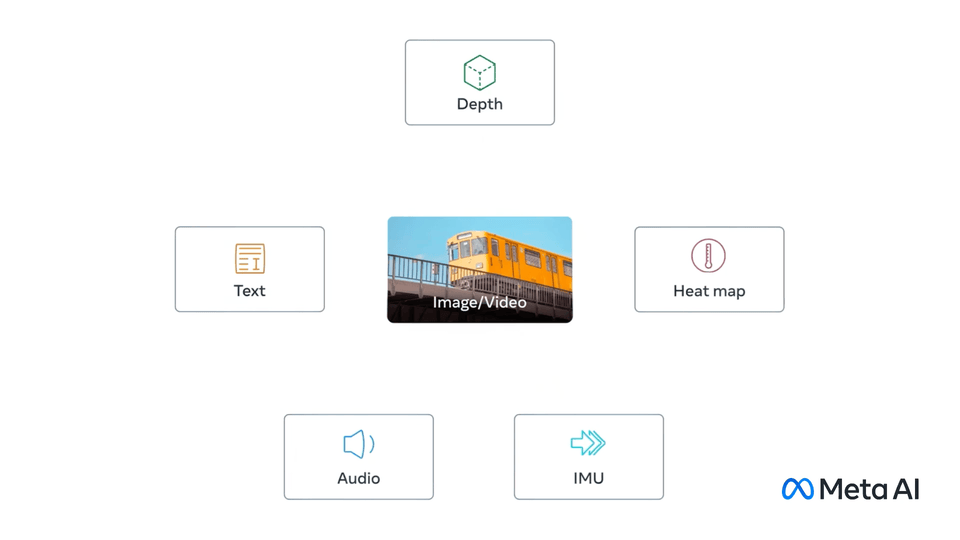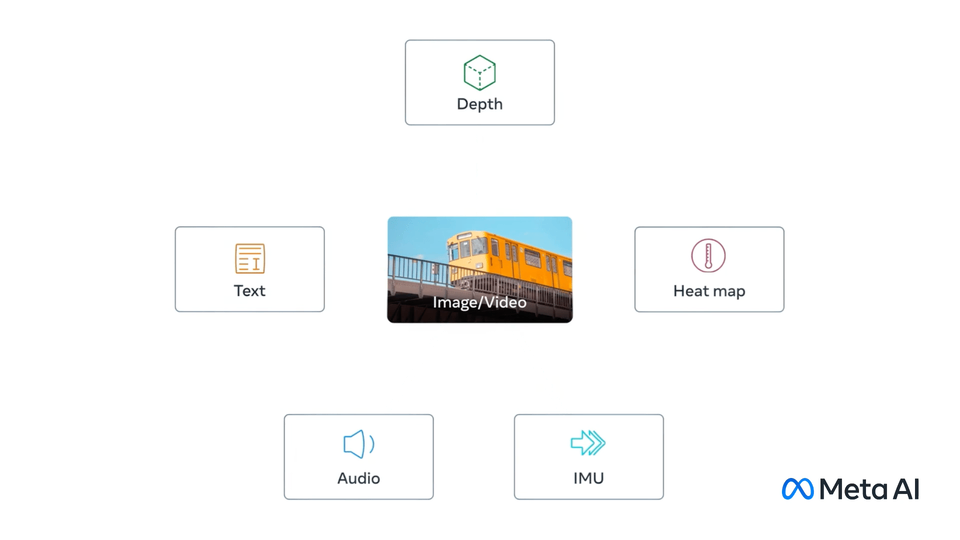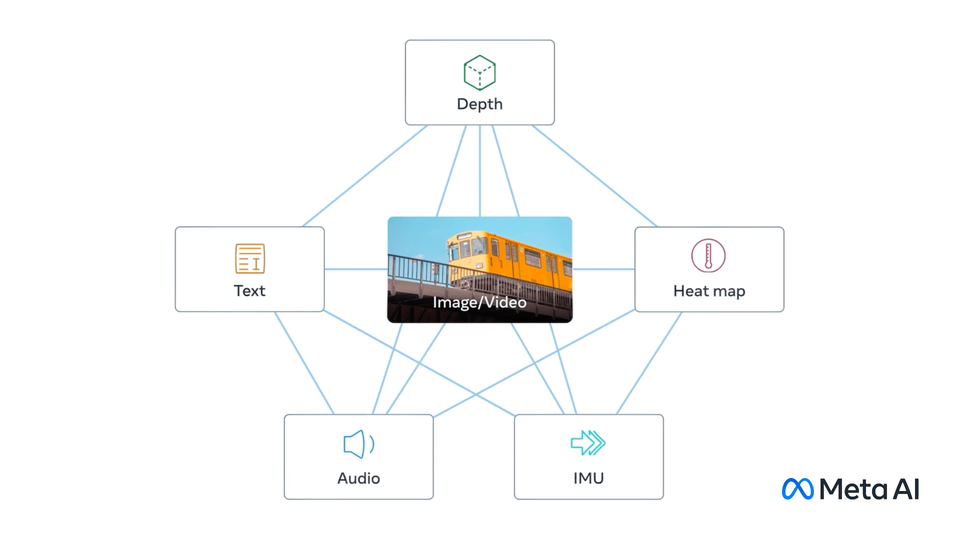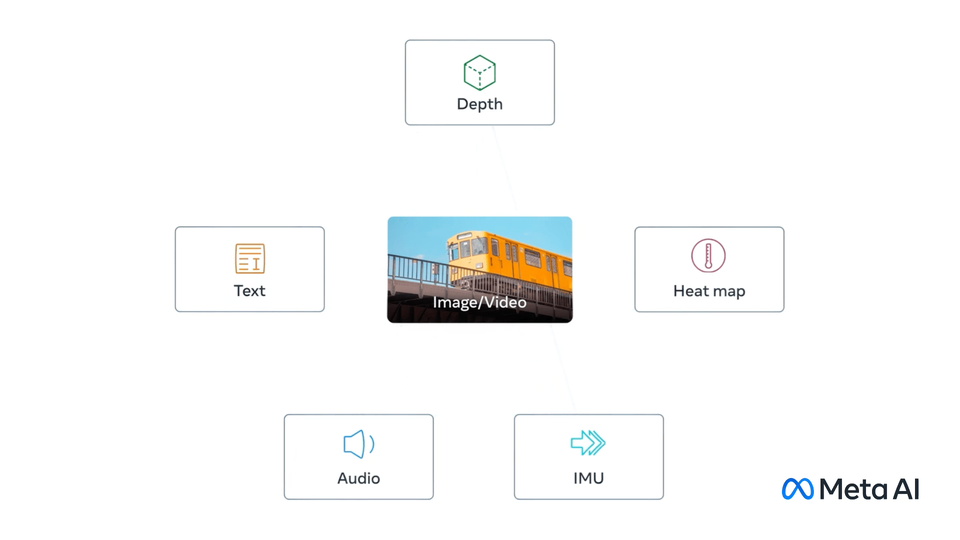
|
||
|
||
## ImageBind model
|
||
|
||
Emergent zero-shot classification performance.
|
||
|
||
<table style="margin: auto">
|
||
<tr>
|
||
<th>Model</th>
|
||
<th><span style="color:blue">IN1k</span></th>
|
||
<th><span style="color:purple">K400</span></th>
|
||
<th><span style="color:green">NYU-D</span></th>
|
||
<th><span style="color:LightBlue">ESC</span></th>
|
||
<th><span style="color:orange">LLVIP</span></th>
|
||
<th><span style="color:purple">Ego4D</span></th>
|
||
<th>download</th>
|
||
</tr>
|
||
<tr>
|
||
<td>imagebind_huge</td>
|
||
<td align="right">77.7</td>
|
||
<td align="right">50.0</td>
|
||
<td align="right">54.0</td>
|
||
<td align="right">66.9</td>
|
||
<td align="right">63.4</td>
|
||
<td align="right">25.0</td>
|
||
<td><a href="https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/imagebind/imagebind_huge.pth">checkpoint</a></td>
|
||
</tr>
|
||
|
||
</table>
|
||
|
||
## Usage
|
||
|
||
Install pytorch 1.13+ and other 3rd party dependencies.
|
||
|
||
```shell
|
||
conda create --name imagebind python=3.10 -y
|
||
conda activate imagebind
|
||
|
||
pip install .
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
For windows users, you might need to install `soundfile` for reading/writing audio files. (Thanks @congyue1977)
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
pip install soundfile
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
Extract and compare features across modalities (e.g. Image, Text and Audio).
|
||
|
||
```python
|
||
from imagebind import data
|
||
import torch
|
||
from imagebind.models import imagebind_model
|
||
from imagebind.models.imagebind_model import ModalityType
|
||
|
||
text_list=["A dog.", "A car", "A bird"]
|
||
image_paths=[".assets/dog_image.jpg", ".assets/car_image.jpg", ".assets/bird_image.jpg"]
|
||
audio_paths=[".assets/dog_audio.wav", ".assets/car_audio.wav", ".assets/bird_audio.wav"]
|
||
|
||
device = "cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
|
||
|
||
# Instantiate model
|
||
model = imagebind_model.imagebind_huge(pretrained=True)
|
||
model.eval()
|
||
model.to(device)
|
||
|
||
# Load data
|
||
inputs = {
|
||
ModalityType.TEXT: data.load_and_transform_text(text_list, device),
|
||
ModalityType.VISION: data.load_and_transform_vision_data(image_paths, device),
|
||
ModalityType.AUDIO: data.load_and_transform_audio_data(audio_paths, device),
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||
embeddings = model(inputs)
|
||
|
||
print(
|
||
"Vision x Text: ",
|
||
torch.softmax(embeddings[ModalityType.VISION] @ embeddings[ModalityType.TEXT].T, dim=-1),
|
||
)
|
||
print(
|
||
"Audio x Text: ",
|
||
torch.softmax(embeddings[ModalityType.AUDIO] @ embeddings[ModalityType.TEXT].T, dim=-1),
|
||
)
|
||
print(
|
||
"Vision x Audio: ",
|
||
torch.softmax(embeddings[ModalityType.VISION] @ embeddings[ModalityType.AUDIO].T, dim=-1),
|
||
)
|
||
|
||
# Expected output:
|
||
#
|
||
# Vision x Text:
|
||
# tensor([[9.9761e-01, 2.3694e-03, 1.8612e-05],
|
||
# [3.3836e-05, 9.9994e-01, 2.4118e-05],
|
||
# [4.7997e-05, 1.3496e-02, 9.8646e-01]])
|
||
#
|
||
# Audio x Text:
|
||
# tensor([[1., 0., 0.],
|
||
# [0., 1., 0.],
|
||
# [0., 0., 1.]])
|
||
#
|
||
# Vision x Audio:
|
||
# tensor([[0.8070, 0.1088, 0.0842],
|
||
# [0.1036, 0.7884, 0.1079],
|
||
# [0.0018, 0.0022, 0.9960]])
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## Model card
|
||
Please see the [model card](model_card.md) for details.
|
||
|
||
## License
|
||
|
||
ImageBind code and model weights are released under the CC-BY-NC 4.0 license. See [LICENSE](LICENSE) for additional details.
|
||
|
||
## Contributing
|
||
|
||
See [contributing](CONTRIBUTING.md) and the [code of conduct](CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md).
|
||
|
||
## Citing ImageBind
|
||
|
||
If you find this repository useful, please consider giving a star :star: and citation
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
@inproceedings{girdhar2023imagebind,
|
||
title={ImageBind: One Embedding Space To Bind Them All},
|
||
author={Girdhar, Rohit and El-Nouby, Alaaeldin and Liu, Zhuang
|
||
and Singh, Mannat and Alwala, Kalyan Vasudev and Joulin, Armand and Misra, Ishan},
|
||
booktitle={CVPR},
|
||
year={2023}
|
||
}
|
||
```
|