10 KiB
@zilliz/claude-context-core
The core indexing engine for Claude Context - a powerful tool for semantic search and analysis of codebases using vector embeddings and AI.
📖 New to Claude Context? Check out the main project README for an overview and quick start guide.
Installation
npm install @zilliz/claude-context-core
Prepare Environment Variables
OpenAI API key
See OpenAI Documentation for more details to get your API key.
OPENAI_API_KEY=your-openai-api-key
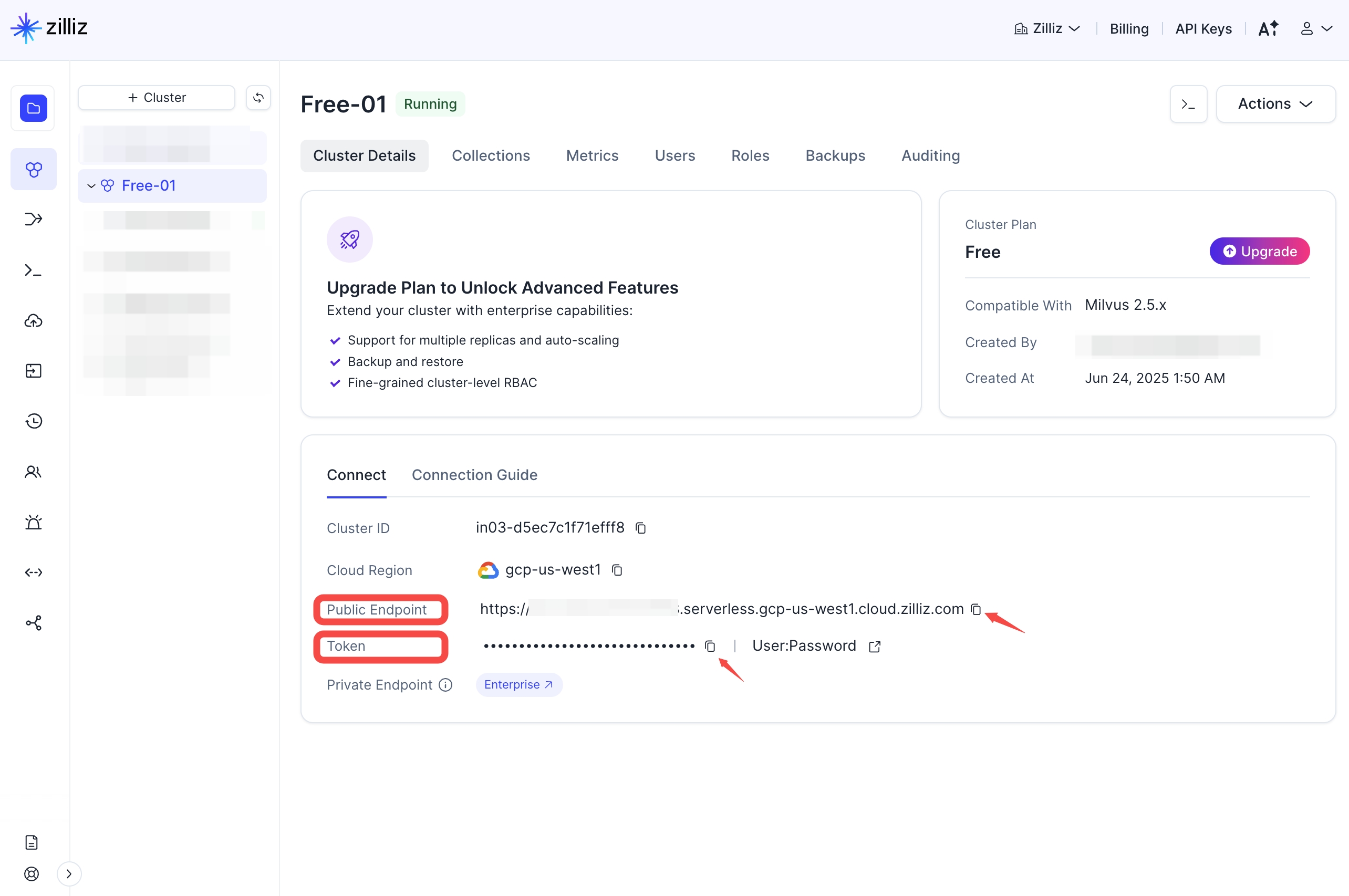
Zilliz Cloud configuration
Get a free Milvus vector database on Zilliz Cloud.
Claude Context needs a vector database. You can sign up on Zilliz Cloud to get a free Serverless cluster.
After creating your cluster, open your Zilliz Cloud console and copy both the public endpoint and your API key.
These will be used as your-zilliz-cloud-public-endpoint and your-zilliz-cloud-api-key in the configuration examples.
Keep both values handy for the configuration steps below.
If you need help creating your free vector database or finding these values, see the Zilliz Cloud documentation for detailed instructions.
MILVUS_ADDRESS=your-zilliz-cloud-public-endpoint
MILVUS_TOKEN=your-zilliz-cloud-api-key
💡 Tip: For easier configuration management across different usage scenarios, consider using global environment variables.
Quick Start
import {
Context,
OpenAIEmbedding,
MilvusVectorDatabase
} from '@zilliz/claude-context-core';
// Initialize embedding provider
const embedding = new OpenAIEmbedding({
apiKey: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY || 'your-openai-api-key',
model: 'text-embedding-3-small'
});
// Initialize vector database
const vectorDatabase = new MilvusVectorDatabase({
address: process.env.MILVUS_ADDRESS || 'localhost:19530',
token: process.env.MILVUS_TOKEN || ''
});
// Create context instance
const context = new Context({
embedding,
vectorDatabase
});
// Index a codebase
const stats = await context.indexCodebase('./my-project', (progress) => {
console.log(`${progress.phase} - ${progress.percentage}%`);
});
console.log(`Indexed ${stats.indexedFiles} files with ${stats.totalChunks} chunks`);
// Search the codebase
const results = await context.semanticSearch(
'./my-project',
'function that handles user authentication',
5
);
results.forEach(result => {
console.log(`${result.relativePath}:${result.startLine}-${result.endLine}`);
console.log(`Score: ${result.score}`);
console.log(result.content);
});
Features
- Multi-language Support: Index TypeScript, JavaScript, Python, Java, C++, and many other programming languages
- Semantic Search: Find code using natural language queries powered by AI embeddings
- Flexible Architecture: Pluggable embedding providers and vector databases
- Smart Chunking: Intelligent code splitting that preserves context and structure
- Batch Processing: Efficient processing of large codebases with progress tracking
- Pattern Matching: Built-in ignore patterns for common build artifacts and dependencies
- Incremental File Synchronization: Efficient change detection using Merkle trees to only re-index modified files
Embedding Providers
- OpenAI Embeddings (
text-embedding-3-small,text-embedding-3-large,text-embedding-ada-002) - VoyageAI Embeddings - High-quality embeddings optimized for code (
voyage-code-3,voyage-3.5, etc.) - Gemini Embeddings - Google's embedding models (
gemini-embedding-001) - Ollama Embeddings - Local embedding models via Ollama
Vector Database Support
- Milvus/Zilliz Cloud - High-performance vector database
Code Splitters
- AST Code Splitter - AST-based code splitting with automatic fallback (default)
- LangChain Code Splitter - Character-based code chunking
Configuration
ContextConfig
interface ContextConfig {
embedding?: Embedding; // Embedding provider
vectorDatabase?: VectorDatabase; // Vector database instance (required)
codeSplitter?: Splitter; // Code splitting strategy
supportedExtensions?: string[]; // File extensions to index
ignorePatterns?: string[]; // Patterns to ignore
customExtensions?: string[]; // Custom extensions from MCP
customIgnorePatterns?: string[]; // Custom ignore patterns from MCP
}
Supported File Extensions (Default)
[
// Programming languages
'.ts', '.tsx', '.js', '.jsx', '.py', '.java', '.cpp', '.c', '.h', '.hpp',
'.cs', '.go', '.rs', '.php', '.rb', '.swift', '.kt', '.scala', '.m', '.mm',
// Text and markup files
'.md', '.markdown', '.ipynb'
]
Default Ignore Patterns
- Build and dependency directories:
node_modules/**,dist/**,build/**,out/**,target/** - Version control:
.git/**,.svn/**,.hg/** - IDE files:
.vscode/**,.idea/**,*.swp,*.swo - Cache directories:
.cache/**,__pycache__/**,.pytest_cache/**,coverage/** - Minified files:
*.min.js,*.min.css,*.bundle.js,*.map - Log and temp files:
logs/**,tmp/**,temp/**,*.log - Environment files:
.env,.env.*,*.local
API Reference
Context
Methods
indexCodebase(path, progressCallback?, forceReindex?)- Index an entire codebasereindexByChange(path, progressCallback?)- Incrementally re-index only changed filessemanticSearch(path, query, topK?, threshold?, filterExpr?)- Search indexed code semanticallyhasIndex(path)- Check if codebase is already indexedclearIndex(path, progressCallback?)- Remove index for a codebaseupdateIgnorePatterns(patterns)- Update ignore patternsaddCustomIgnorePatterns(patterns)- Add custom ignore patternsaddCustomExtensions(extensions)- Add custom file extensionsupdateEmbedding(embedding)- Switch embedding providerupdateVectorDatabase(vectorDB)- Switch vector databaseupdateSplitter(splitter)- Switch code splitter
Search Results
interface SemanticSearchResult {
content: string; // Code content
relativePath: string; // File path relative to codebase root
startLine: number; // Starting line number
endLine: number; // Ending line number
language: string; // Programming language
score: number; // Similarity score (0-1)
}
Examples
Using VoyageAI Embeddings
import { Context, MilvusVectorDatabase, VoyageAIEmbedding } from '@zilliz/claude-context-core';
// Initialize with VoyageAI embedding provider
const embedding = new VoyageAIEmbedding({
apiKey: process.env.VOYAGEAI_API_KEY || 'your-voyageai-api-key',
model: 'voyage-code-3'
});
const vectorDatabase = new MilvusVectorDatabase({
address: process.env.MILVUS_ADDRESS || 'localhost:19530',
token: process.env.MILVUS_TOKEN || ''
});
const context = new Context({
embedding,
vectorDatabase
});
Custom File Filtering
const context = new Context({
embedding,
vectorDatabase,
supportedExtensions: ['.ts', '.js', '.py', '.java'],
ignorePatterns: [
'node_modules/**',
'dist/**',
'*.spec.ts',
'*.test.js'
]
});
File Synchronization Architecture
Claude Context implements an intelligent file synchronization system that efficiently tracks and processes only the files that have changed since the last indexing operation. This dramatically improves performance when working with large codebases.
How It Works
The file synchronization system uses a Merkle tree-based approach combined with SHA-256 file hashing to detect changes:
1. File Hashing
- Each file in the codebase is hashed using SHA-256
- File hashes are computed based on file content, not metadata
- Hashes are stored with relative file paths for consistency across different environments
2. Merkle Tree Construction
- All file hashes are organized into a Merkle tree structure
- The tree provides a single root hash that represents the entire codebase state
- Any change to any file will cause the root hash to change
3. Snapshot Management
- File synchronization state is persisted to
~/.context/merkle/directory - Each codebase gets a unique snapshot file based on its absolute path hash
- Snapshots contain both file hashes and serialized Merkle tree data
4. Change Detection Process
- Quick Check: Compare current Merkle root hash with stored snapshot
- Detailed Analysis: If root hashes differ, perform file-by-file comparison
- Change Classification: Categorize changes into three types:
- Added: New files that didn't exist before
- Modified: Existing files with changed content
- Removed: Files that were deleted from the codebase
5. Incremental Updates
- Only process files that have actually changed
- Update vector database entries only for modified chunks
- Remove entries for deleted files
- Add entries for new files
Contributing
This package is part of the Claude Context monorepo. Please see:
- Main Contributing Guide - General contribution guidelines
- Core Package Contributing - Specific development guide for this package
Related Packages
- @claude-context/mcp - MCP server that uses this core engine
- VSCode Extension - VSCode extension built on this core
License
MIT - See LICENSE for details